Astronomical Basics of the Solstice
The exact definition is: The summer solstices are the times in which the apparent geocentric ecliptic longitude of the Sun is 90° or 270°. “Apparently” means taking account of nutation and aberration. “Geocentric” means seen by a fictitious observer at the center of the Earth. The definition is independent of the location of a real observer, hence the solstices occur at the same time a world (but different depending on the local time zone corresponds times).
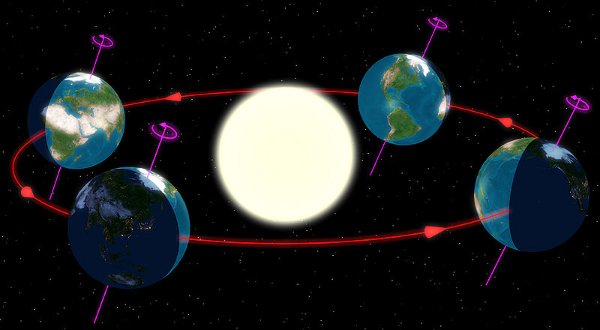
The two time points fall within a few minutes with those times together where the sun its greatest northern or southern declination – about 23° 26′ 20″ – and thus reaches its northernmost or southernmost position in the celestial sphere, the small time difference results from the fact that it really is the center of mass of the earth / moon system, which evenly in the “Earth” ground plane (ecliptic) moves around the sun, while the earth itself orbits this center of gravity and is usually slightly above or below this level is located. Geozentrum as seen from the sun, therefore, does not exactly on the ecliptic (ecliptic latitude she has a non-zero). happens to you for a reason not exactly the northernmost or southernmost point of the ecliptic, on the other performs its variable ecliptic latitude to that the maximum declination is generally not accepted exactly the solstice points.